Background:
Many water utilities around the world have been suffering for years from underinvestment, alongside significant deterioration of the water system due to aging infrastructure and inadequate maintenance. Today, water utilities face additional challenges, such as increased water consumption coupled with a decrease in water sources due to extreme climatic events, pollution, and inefficient management of existing systems. Additionally, there is a need to enhance control and monitoring of all water systems to ensure a continuous supply of safe drinking water to the entire population. This challenge is even greater in rural and remote areas, where there are additional issues such as resource scarcity, lack of skilled manpower, rising operational costs, and limited budgets.
To address these challenges, it is necessary to focus on two levels: the operational level and the data management level.
At the operational level, we can define five main challenges:
• Intermittent water supply
• Limited maintenance and service levels
• Lack of automation, remote monitoring, and control, resulting in a lack of real-time data
• Delayed response to critical events, causing significant damage and expenses
• Limited or non-existent corporate governance, both at the utility and state/national levels
In terms of data challenges, there was a time when the primary issue was the insufficient data available about the operation within the water network. However, today, the capacity to gather real-time data from the field is virtually limitless. This abundance of information introduces new challenges related to managing this data and utilizing it in real-time to address the operational challenges previously mentioned.
The first step in improving the operation of water systems lies in the real-time collection and management of relevant and accurate data from remote facilities. Considering this, the characteristics required of data management systems in water corporations include the following parameters:
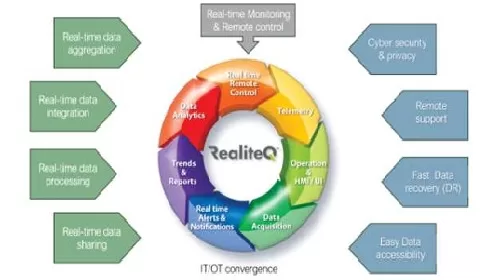
• Real-time data collection from all critical sites
• Real-time monitoring and remote control
• Real-time data aggregation
• Real-time data integration
• Real-time data processing
• Real-time data sharing
Additionally, we must address the cyber security challenge due to global threats to strategic facilities, including water systems.
The digital transformation challenge:
Digital transformation is the integration of the physical-operational layer with the digital informational layer. It involves incorporating Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud computing technologies into an organization to enhance control, safety, efficiency, productivity, and ultimately improve the organization’s operations and business outcomes.
Without a doubt, digital transformation represents the most significant revolution in the water market since the introduction of control and automation technologies.
In 2016, GWI magazine published a report highlighting that the water and wastewater industry is transitioning to a digital revolution. Digital transformation is a game changer for water utilities, adding value by connecting real-time data, people, and processes.
However, a recent publication by the SWAN forum stated, “The United States represents the epicentre of the global digital economy, at least in terms of technology development and go-to-market strategies. The U.S. municipal water sector, however, has lagged its peers in other advanced economies” (Smart Water Report, SWAN).
This phenomenon characterizes not only the water companies in the USA but is typical of a considerable part of the water companies around the world. Various studies point to a variety of reasons for this, but all agree on three main factors contributing to the slow adoption of the digital transformation process:
• Cost (construction and maintenance)
• Technological complexity (installation, maintenance, and use) due to a lack of skilled teams
• Information security (especially cyber protection)
To address these challenges and simplify the digital transformation process while ensuring it remains secure and affordable for all, a fifth market segment has been introduced in recent years. This segment offers comprehensive cloud software and IoT hardware solutions that span from the infrastructure level, including communication, up to the ICT and SCADA systems level, and extend to cybersecurity and data analytics. This market segment is developing at a fast pace and is led by RealiteQ”. (Frost & Sullivan) in this article we will present a case study of implementation of digital transformation in large water utility with decentralized system, using most advanced holistic platform.
Case study: digital transformation implementation in water utility
Background:
The Water Commission of the State of Mexico – CAEM, is a decentralized public entity known as the “State Commission for Water and Sanitation,” with its own legal status and assets. Its general purpose is to build, maintain, operate, and manage potable water and sewer systems for the benefit of urban and rural communities in the State of Mexico. Essentially, it is responsible for the distribution of potable water in the State of Mexico and its municipalities, and thus operates specialized facilities for the storage, distribution, and exploitation of potable water wells.
In the second half of 2019, there was an overflow in one of the most important water storage tanks in the eastern area of the State of Mexico. This situation presented the first opportunity to demonstrate the effectiveness of process automation in water management facilities through real-time remote control and monitoring via the IIoT platform from RealiteQ. This initiative started with the Cerro Gordo tank located in the municipality of Ecatepec, which has now become possibly the largest project in Mexico in terms of the number of installations controlled remotely and in real time.
The organization’s management was aware of the technology offered by RealiteQ through prior work with our local solutions integrator, who immediately proposed a plan to eliminate the operational risk of continued tank overflows due to operational errors, primarily caused by the lack of personnel or the handling of valves and pumping equipment at specific times.
Within a week, our local integrator implemented the improvement plan, which involved automating the tank’s operational processes. Manual measurements were replaced with a complete set of digital sensors to obtain tank levels, start and stop pumping equipment, gather data from various flow meters installed in the network, and automated valves to control flow based on operational directives defined by CAEM management according to water distribution needs. Since then, the Cerro Gordo tank has been remotely controlled in real-time and operates autonomously according to operational guidelines, minimizing personnel intervention. As a result, there have been no tank overflows since it began operating automatically through the RealiteQ platform.
About RealiteQ Scada 4.0 holistic platform
RealiteQ Scada 4.0 – Bundle of IOT & cloud programs & tools from the infrastructure level through the ICT, SCADA level and up to the Cybersecurity & data analytics level for real time, remote-control operation & Data management.
RealiteQ is a Holistic solution for digital transformation – single-source solution of IIoT hardware and Cloud software from the infrastructure level through the ICT & SCADA level and up to the Cybersecurity & data analytics level, providing a comprehensive solution for real-time, Secured, remote-control operation & Data management from “A” to “Z” (Data acquisition, telemetry, real-time & historian data management, Alert & Notification, data analytics & BI, cybersecurity, remote control & visualization) of devices, sites, facilities, and the entire networks.
RealiteQ allowing real-time interfacing between all the different devices from different manufacturers on site and connecting all sites in the network together, allowing data sharing and improve the transparency within the utility to provide the highest quality information to the operational level and decision makers.
The technology consists of four system components:
• ICEX (Integrated Cellular and Ethernet Explorer) – Smart gateway installed in remote sites.
• COMP (Central Online Management Portal) – Mediates communication, data, security & users.
• UI – Browser-based graphical user interface (HMI/SCADA)
• VPN – for remote secured accesses to PLC on remote sites
RealiteQ is on the one hand, the most advanced solution existing today but on the other hand, it is simple to install, use and maintain, it is highly secured, and most importantly it is affordable to any organization from the smallest to the largest.
Scope of work:
With the evidence of efficiency in managing such installations, CAEM decided to extend the pilot project to its entire network and for that they have been engaged with APRA – a Mexican company dedicated to offering end-to-end comprehensive solutions. The collaboration model designed for CAEM is an integral service that develops the process automation plan, transitioning from manual/analog to digital operation, and is responsible for the equipment, maintenance, and replacement of all necessary components for the operation of the automation system. This ensures that each component functions adequately and that those that fail are replaced as quickly as possible, ensuring uninterrupted operation once a facility is automated. Additionally, APRA handles all the design work of automated processes and their programming, as well as the initial configuration of the platform and the multiple control dashboards.
The service is complemented by ongoing training for users authorized by CAEM management.
The project includes
• Installation of electrical and communication network engineering to comply with the project specifications at each site.
• Automation configuration: networking, device programming, provision of various measuring instruments and sensors.
• 24/7 permanent maintenance of the automation system: maintenance and replacement of any device required in the operation of the tanks.
• Remote monitoring and control of site operation 24/7 from any place.
• All sites are connected to one centralized remote monitoring and control system.
The project objectives:
• Remote monitoring and control of site operation 24/7 from any place.
• The facility can be operated under the guidelines authorized by Operations DG remotely and in real time, without restriction of schedules or the distance it is.
• Values of all measured and controlled parameters are presented in real time in an intuitive, easy to follow manner. Historical data of important measured parameters enables optimizing of different parts and the whole process.
Over the past four years, the original scope of process automation for potable water management has expanded to various types of installations in more than 120 facilities.
Currently, CAEM controls via the RealiteQ wide range of facilities including:
• Water storage tanks with capacities up to 50,000 cubic meters
• Water conveyance lines with diameters up to 60 inches over dozens of kilometers
• Pumping plants
• Monitoring of pressure in conveyance lines at critical points
• Automated valves controlled by target flow or specific volume across different communities or urban areas
• Deep potable water wells where the production of each installation and the status of their assets, such as pump motors, are monitored
• Water Treatment Plant
• Weather stations for monitoring climatological variables, mainly rainfall.
As part of the solution CAEM have all the tools they need to improve the operational efficiency of the connected facilities using RealiteQ UI which includes, operational dashboards, trends, tables, smart alert and notification system, BI dashboards.
Results & outcome:
Using RealiteQ not only allow to have real-time monitoring and remote control (SCADA) of the remote facilities, but it also provides:
IT/OT convergence (real-time data integration)- Real-time processing & integrates information technology (IT) with operational technology (OT) used to monitor events, processes, and devices, adjusts in networks sites, machines, enterprise and industrial operations and offers significant benefits in cost, quality, speed and reliability.
Data management – RealiteQ platform is much more than just a remote-control platform, it is a real-time data management system from A to Z, from the data acquisition to Big data analytics. By using RealiteQ you are not only operating and controlling the system in real-time, but you also can use the data to increase efficiency.
Data Aggregation – Real time Data aggregation and data analysis to improve the utility operational efficiency is one of the biggest challenges water utilities are facing today, RealiteQ makes it available, accessible, and affordable to any utility by providing real-time secured IT/OT convergence.
Real time display of assets health – RealiteQ provides for real time graphic display (on a Google map and more) of the status of each of the devices (assets) connected using a dashboard display.
Smart alerts system – Highly advanced mechanism for managing faults. Each fault may be defined as a fault that requires a confirmation action, deliberate faults may be silenced for an extended time, there is no limit to the number of faults or the number of fault recipients, a “nagging” mechanism may be used for recurrent alerts until the problem is resolved, and there is an alert escalation mechanism, ensuring that it is transferred to a number of parties based on the priority for remedial action and responsibility.
Secure hierarchical system – The Comprehensive Cloud based SCADA system allows for connection of local systems to a secure hierarchical central system at the country (and even global) level. The system allows for access by an unlimited number of users (according to personal authorizations) while building a clear hierarchy from the worker on the ground to the facility level, network operator, regional manager to the entire country and world.
The project was very successful and the main CAEM has achievements from the project were:
• Increase in safety in the operating guidelines
• Reduce operational costs
• Reduce water loss
• Save energy
• Service without interruption.
• Stability in different basic parameters, such as:
• Storage levels.
• Exact water consumption for each circuit
• Eliminating the overflow of storage tank
• Reducing emergency response times
• Operating water distribution circuits remotely
• Having information on operational trends of different installations
• Sharing critical potable water availability information with municipalities.
Costumer testimony (CAEM – Ing. Salvador Ibarra. Director of Facilities Maintenance):
• The communication between different CAEM’s areas improved given a better, quicker and accurate information flow about several performance operative variables produced at facilities level.
• Better control and efficiency in water distribution. Now we can determine target flows at specific times and areas of the city based on hard and accurate data in real time using the ReliteQ’s Central Management Online Portal.
• Improved relationship with community leaders. We can share with the community and its representatives accurate and reliable information about the flows that are delivered in certain periods of time at different seasons of the year and demonstrate that we comply with the agreed commitments.
• With RealiteQ the time to attend municipal authorities’ requirements for the distribution of drinking water has improved significantly because now from the central online management portal we can change the flows in different conduction lines simultaneously and in real time, having the ability to respond immediately to the demands of the community.
• Reduction of maintenance costs. We have reduced total stop hours at facilities due to the failure of pumping equipment. With the RealiteQ platform it is possible to permanently monitor the main performance variables of the pumping equipment and determine in advance when any equipment requires repair.
• We achieved the elimination of the risk of flooding of facilities due to sudden excess inflow that are greater than storage tank capacity, it resulted in the total loss of expensive water pumps and electrical installations.
• The use of the RealiteQ Platform allows us to operate our facilities in a safer environment for our collaborators. Before RealiteQ, it was normal to send personnel to facilities far from the city to manipulate valves or pumps at night and in high-risk areas in security terms. Now all facilities inflows and outflows are monitored at any time by the responsible personnel.
Conclusion
I believe that the solution presented in this article and the successful case study is very relevant for the water market in India (cities as well as remote rural villages) as well as many other areas in the world who suffered from all of some of the challenges described in this article.
This corresponds very closely with the priorities set by the Government of India and the initiatives that the Government of India has been leading in recent years. The government of India’s focus on improving water management and conservation, as well as increasing access to clean water for all citizens. The government is encouraging and investing in digital transformation initiatives in the water utilities sector.
One of the main initiatives for digital transformation in the water utilities sector in India is the “Smart Cities Mission” focuses on the use of digital technologies to improve the quality of life and service delivery in the cities.
Another initiative is the “AMRUT” (Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation) and “AMRUT 2.0 scheme, which aims to provide basic infrastructure in 500 cities and towns across India. The scheme also focuses on the use of digital technologies to improve water management and distribution.