Water is often taken for granted, yet for many around the globe, it is a precious and increasingly scarce resource. As populations grow and climate change disrupts traditional water cycles, the availability of fresh water is becoming a critical concern. The World Health Organization reports that over 2 billion people live in countries experiencing high water stress. In response, the world is turning to the ocean, which covers over 70% of our planet, as a vast and largely untapped source of fresh water through the process of desalination. Desalination, the process of removing salt and impurities from seawater to produce fresh drinking water, has emerged as a vital solution in regions where freshwater is scarce. Countries like Saudi Arabia and Israel have long relied on desalination to meet a significant portion of their water needs, with Israel deriving about 55% of its domestic water from desalinated sources. Globally, the desalination market has grown rapidly, with over 20,000 desalination plants now in operation, producing nearly 100 million cubic meters of desalinated water each day. However, despite its promise, traditional desalination methods are not without challenges. The energy-intensive nature of the process, coupled with environmental concerns such as the disposal of brine—a byproduct of desalination—limits its broader adoption. As a result, there is a growing need for innovative technologies that can make desalination more efficient, sustainable, and accessible.
In this article, exploration of the latest breakthroughs in desalination technology, examining how new methods are addressing the limitations of traditional approaches. From harnessing solar energy to creating electricity-free systems, these innovations promise to unlock new possibilities for securing the world’s freshwater future.
Challenges in traditional desalination methods
Traditional desalination methods, such as reverse osmosis and thermal distillation, have been the backbone of seawater conversion for decades. However, these methods come with substantial challenges that hinder their widespread adoption and sustainability. One of the most pressing issues is the high energy demand. Reverse osmosis, the most common desalination technique, requires enormous amounts of electricity to push seawater through membranes that filter out salt. This process not only drives up operational costs but also raises environmental concerns, particularly in regions where energy is sourced from fossil fuels. Moreover, the issue of membrane fouling—where contaminants build up on the membranes, reducing efficiency and increasing maintenance costs—further complicates the operation. In addition to energy consumption and fouling, the disposal of brine, the highly concentrated saltwater left over after desalination, poses a significant environmental risk. Discharging brine back into the ocean can harm marine ecosystems, leading to long-term ecological damage. These challenges highlight the need for innovative solutions that can make desalination more efficient, environmentally friendly, and economically viable.
Membrane fouling
Membrane fouling is one of the most persistent and challenging issues in the operation of reverse osmosis (RO) desalination systems. Fouling occurs when particles, microorganisms, or other contaminants accumulate on the surface of the desalination membranes, leading to a significant decline in system performance. Over time, these deposits can clog the membranes, reducing water flow, increasing the energy required to push water through the system, and ultimately leading to a reduction in the overall efficiency of the desalination process. The impact of membrane fouling extends far beyond just a decrease in performance. Fouling necessitates frequent maintenance, including chemical cleaning and, in severe cases, membrane replacement. This maintenance not only incurs substantial costs but also results in downtime, during which the plant cannot produce fresh water. For instance, the cost of membrane replacement alone can be a significant financial burden, particularly for large-scale desalination plants, which may contain thousands of individual membrane modules.
Innovative desalination technologies
As traditional desalination methods grapple with challenges such as high energy consumption and membrane fouling, the search for innovative solutions has become more urgent. New technologies are emerging that promise to overcome these obstacles, offering more efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective ways to turn seawater into fresh, drinkable water. These innovations are not merely incremental improvements but represent a fundamental shift in how desalination can be approached, potentially transforming the landscape of water security. From electricity-free methods that harness natural temperature gradients to advanced solar-powered systems, these technologies are paving the way for a future where desalination is more accessible to all, particularly in regions most vulnerable to water scarcity. As we explore these cutting-edge developments, it becomes clear that innovation is not just a luxury but a necessity in the quest to meet the world’s growing water needs.
• Thermodiffusive Desalination
Thermodiffusive desalination represents a groundbreaking advancement in the quest for more efficient and sustainable methods of converting seawater into fresh water. Developed by researchers at the Australian National University, this innovative technique stands out for its simplicity and effectiveness. Unlike traditional desalination processes that rely on complex machinery and energy-intensive operations, thermodiffusive desalination leverages low-temperature heat from the environment, operating entirely in the liquid phase without the need for phase changes or membranes. The core mechanism of thermodiffusive desalination involves passing seawater through a narrow channel that is heated on one side and cooled on the other. This temperature difference causes a separation of water based on salinity, with less saline water migrating toward the warmer side and more saline water toward the cooler side. Through repeated cycles, the salinity of the water is gradually reduced, producing fresh water that meets the needs of agriculture and other critical uses. The absence of a membrane in this process is particularly noteworthy, as it eliminates the common problem of membrane fouling—a significant operational challenge in traditional reverse osmosis systems. This technology’s potential extends far beyond just operational efficiency. Its simplicity and reliance on naturally available temperature gradients make it especially well-suited for deployment in regions suffering from severe drought or those with limited access to electricity. For instance, the researchers are already testing the system on the Pacific island of Tonga, where it is powered by a small solar panel. This adaptability and low environmental impact make thermodiffusive desalination a promising solution for providing water security in some of the world’s most vulnerable areas. The development of thermodiffusive desalination underscores the importance of rethinking our approach to water purification. By harnessing natural forces in innovative ways, this technology offers a path forward that is not only sustainable but also accessible, addressing both the technical and humanitarian challenges of ensuring a reliable supply of fresh water in an increasingly water-scarce world.
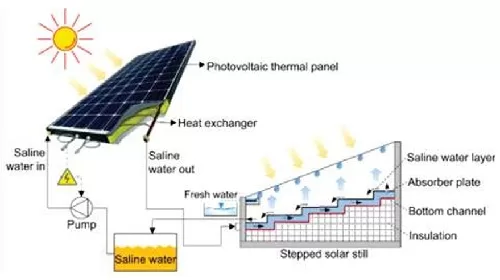
• Solar-Powered Multistage Desalination
One of the most promising innovations in desalination technology comes from researchers at MIT, who have developed a solar-powered multistage desalination system. This cutting-edge method offers a sustainable solution by utilizing solar energy to drive the desalination process, which could drastically reduce the cost of producing freshwater, making it even cheaper than tap water. The mechanism behind this technology is inspired by the natural process of thermohaline convection, a phenomenon that occurs in the world’s oceans where variations in temperature and salinity drive water circulation. The MIT system replicates this on a smaller scale, using a multistage process that combines evaporation and condensation to separate salt from seawater. The system consists of several stages, each designed to enhance the circulation of water and salt, mimicking the natural convection currents found in the ocean. As seawater flows through these stages, it is heated by solar energy, causing the water to evaporate, leaving the salt behind. The water vapor is then condensed into fresh, drinkable water. This multistage approach not only increases the efficiency of the desalination process but also extends the operational life of the system. By preventing the buildup of salt within the system, which is a common problem in traditional desalination methods, this technology can operate for years without significant maintenance, further reducing costs. The researchers have demonstrated that this system can produce up to 5 liters of freshwater per hour per square meter of solar collection area, making it a viable option for regions with high solar irradiance. The cost-effectiveness of this solar-powered system is particularly noteworthy. Because it relies on solar energy, it eliminates the need for expensive and environmentally damaging fossil fuels. The operational costs are so low that, for the first time, desalinated water could be produced at a cost lower than that of tap water in the United States. This breakthrough has profound implications, especially for regions where access to fresh water is limited by both geographic and economic factors. The system’s long lifespan and minimal maintenance requirements make it an attractive option for both developed and developing regions, offering a sustainable solution to the global challenge of water scarcity. By tapping into the abundant energy of the sun, this solar-powered desalination technology represents a significant step forward in the quest for sustainable, affordable, and accessible freshwater. It highlights the potential of innovative approaches to not only address the technical challenges of desalination but also to make it economically viable on a global scale.
• Electricity-Free Desalination
In the relentless pursuit of sustainable water solutions, a groundbreaking method developed in collaboration with Shanghai Jiao Tong University has emerged: electricity-free desalination. This innovative approach offers a viable alternative for regions where access to electricity is either limited or prohibitively expensive, addressing one of the most significant barriers to the widespread adoption of traditional desalination technologies. The electricity-free desalination system operates using natural convection processes, a fundamental physical phenomenon where fluid motion is driven by temperature differences. In this system, seawater is heated naturally—often through solar energy—causing it to rise as it becomes less dense. The warmer, less salty water moves to the upper layers, while the cooler, saltier water sinks. This separation of water based on temperature and salinity allows for the gradual reduction of salt content as the water cycles through the system. This natural convection process is not only energy-efficient but also eliminates the need for complex machinery or electrical inputs, making the system highly adaptable to various environmental conditions. The modular design of this electricity-free desalination system is another key advantage. Its simplicity allows for easy scalability, from small, household-sized units to larger systems capable of supplying fresh water to entire communities. This flexibility is particularly important in remote or rural areas where infrastructure is limited, and the need for a reliable, low-maintenance water source is critical. The system’s ability to function without electricity also makes it an ideal solution for disaster-stricken areas, where access to power may be disrupted. Moreover, the environmental benefits of this technology are significant. By eliminating the need for electricity, the system reduces carbon emissions and lowers the overall environmental footprint of desalination operations. This makes it a more sustainable option for long-term water management, particularly in regions that are already vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. The potential of electricity-free desalination extends far beyond individual applications. As the global demand for fresh water continues to rise, particularly in developing countries, this technology offers a promising path forward. Its scalability, low environmental impact, and ability to operate independently of the electrical grid make it a critical innovation in the ongoing effort to provide clean, accessible water to al. By reimagining the fundamentals of water purification, the electricity-free desalination method stands as a testament to the power of innovation in addressing some of the most pressing challenges of our time. It offers a new horizon in the field of desalination, one that is both inclusive and sustainable, paving the way for a future where fresh water is within reach for everyone, regardless of their location or economic status.
• Economic Feasibility and Cost Considerations
When considering the large-scale deployment of innovative desalination technologies, cost remains a critical factor. Traditional desalination methods, such as reverse osmosis (RO), have long been associated with high operational costs, driven primarily by energy consumption and maintenance requirements. The financial burden of these systems often makes them less accessible, particularly in developing regions where budget constraints are a significant concern. In contrast, newer technologies are demonstrating potential for significant cost savings, both in terms of operational expenses and initial investment. Additionally, the absence of membranes in this system reduces maintenance costs, as there is no need for frequent replacements or chemical cleaning. Similarly, the solar-powered multistage desalination system from MIT is designed with cost-effectiveness in mind. By utilizing solar energy, the system eliminates the need for electricity, which is a major cost driver in traditional desalination. The long operational life of this system, coupled with its minimal maintenance needs, further enhances its economic appeal. Researchers estimate that this technology can produce freshwater at a cost lower than that of tap water in the United States, positioning it as a viable solution for both developed and developing markets. The electricity-free desalination method developed in collaboration with Shanghai Jiao Tong University also offers promising economic advantages. This system’s ability to operate without electricity not only reduces energy costs but also makes it particularly suitable for deployment in remote or off-grid areas where access to electricity is limited. The modular design of this system allows for scalable deployment, meaning it can be tailored to meet the specific needs and budget constraints of different communities, from small households to large-scale operations. However, the initial capital costs associated with these innovative technologies remain a consideration. While the long-term savings in operational and maintenance costs are significant, the upfront investment required for infrastructure, especially in scaling up production and distribution, can be a barrier. This is where government subsidies, international aid, and private investment become crucial. Programs aimed at promoting sustainable technologies, such as the European Union’s Green Deal, can provide the financial support needed to offset initial costs and accelerate the adoption of these advanced desalination methods.
• Potential Applications and Impact
As innovative desalination technologies continue to evolve, their potential applications and impact on global water security become increasingly clear. These advancements are not confined to theoretical improvements; they offer practical solutions to some of the world’s most pressing challenges. From providing reliable water sources in drought-prone regions to supporting agriculture in arid climates, the applications of these technologies are vast and varied. Moreover, their impact extends beyond mere water production, influencing economic development, public health, and environmental sustainability. In this section, we will explore how these cutting-edge desalination methods can be deployed in various contexts, examining their potential to transform lives, economies, and ecosystems across the globe
• Securing the Future: Global Water Security
The promise of innovative desalination technologies extends far beyond the developed world, holding particular significance for developing countries grappling with severe water scarcity. In many of these regions, access to clean, potable water remains a daily struggle, exacerbated by climate change, population growth, and limited infrastructure. For nations facing such challenges, the ability to harness the ocean’s vast resources through sustainable desalination could be transformative. These technologies offer a lifeline to communities where traditional water sources are unreliable or entirely absent. For example, in sub-Saharan Africa, where millions of people rely on seasonal rivers or groundwater that is often contaminated, deploying solar-powered or electricity-free desalination systems could provide a consistent and safe water supply. The adaptability of these technologies is crucial; systems like those developed by MIT or in collaboration with Shanghai Jiao Tong University can be scaled to fit the needs of small villages or entire cities, making them versatile tools in the fight against water scarcity. Moreover, the reduced operational costs and minimal maintenance requirements of these advanced systems make them economically feasible for regions with limited financial resources. Traditional desalination methods often require significant investment in both capital and ongoing energy costs, making them less accessible for poorer nations. In contrast, the energy efficiency and sustainability of newer technologies mean that even areas with limited infrastructure can benefit from clean water at a lower cost, without the heavy reliance on external power sources. This is particularly important in regions where electricity is scarce or prohibitively expensive.
• Nurturing Growth: Agriculture and Industry
The role of water in agriculture cannot be overstated, particularly in regions where water scarcity directly threatens food security and economic stability. As climate change exacerbates drought conditions and depletes traditional water sources, the need for reliable and sustainable irrigation solutions becomes increasingly urgent. Innovative desalination technologies offer a promising solution to these challenges, providing a steady supply of fresh water that can support agricultural production even in the most arid environments. The potential impact on industry is equally significant. In sectors such as mining, manufacturing, and energy production, where water is a critical input, the availability of desalinated water could ensure continuity of operations even during periods of severe drought. Industries that are currently limited by water availability could expand, leading to job creation and economic growth. Moreover, the ability to use desalinated water for industrial processes could reduce the pressure on freshwater resources, preserving them for human consumption and environmental sustainability. The economic benefits of integrating desalination into agriculture and industry extend beyond mere water supply. The cost savings associated with using efficient desalination technologies, such as those powered by solar energy, can lower the overall expenses of water-intensive operations. This not only makes desalinated water a viable alternative but also an economically attractive one. Furthermore, as these technologies continue to advance and become more affordable, their adoption could drive a broader transformation in how water is sourced and used across various sectors. In summary, the application of innovative desalination technologies in agriculture and industry holds the potential to reshape water use practices in regions facing severe water scarcity. By ensuring a reliable and cost-effective supply of fresh water, these technologies could safeguard food security, support industrial growth, and contribute to economic resilience in some of the world’s most vulnerable areas. The broader adoption of these technologies could thus play a crucial role in addressing both current and future water challenges, helping to secure a sustainable and prosperous future for communities worldwide.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the potential applications of innovative desalination technologies in disaster relief and emergency use are profound. These systems offer a practical and effective solution to one of the most pressing challenges in disaster management-ensuring that affected populations have access to clean, safe water when they need it most. By integrating these technologies into disaster preparedness and response strategies, governments and aid organizations can significantly enhance their ability to respond to crises, ultimately saving lives and supporting faster recovery.