Water is a crucial element for sustaining life. The swift expansion of population, urbanization, irrigation, and industrialization has exerted immense pressure on water resources. The combined effect of escalating usage of this invaluable natural resource has given rise to water scarcity in numerous regions across the globe with several countries facing difficult challenges. In India, almost 44% of the population is facing extreme water stress, reported by the Niti Aayog. Moreover, climate change has contributed to alterations in the hydrological cycle within the nation. Therefore, safeguarding this scarce resource requires…
Read MoreCategory: Tech 2.0
Urban and Industrial Sustainable Water Management: A Collective Responsibility
Introduction: The finite nature of water resources and their susceptibility to pollution, contamination, and climatic influences underscore the pressing need for strategic interventions to ensure sustainable usage. The Sustainable Development Goal’s target 6.4, recognizes this challenge and demands increased water efficiency which is a way of easing water demand pressure/water user conflict by more effectively utilizing every unit of existing supply. Urban areas, in particular, grapple with burgeoning demands, prompting the imperative adoption of water conservation practices capable of reducing consumption by up to one-third, concurrently mitigating surface and groundwater…
Read MoreCONSTRUCTED WETLANDS: A WASTEWATER TREATMENT TECHNOLOGY AND ITS SCOPE IN INDIAN AGRICULTURE
By Rama Pal, S. Islam, M. Muruganandam, Vibha Singhal, Trisha Roy and Uday Mandal ICAR-Indian Institute of Soil and Water Conservation IntroductionToday we face challenges of water scarcity, wastewater discharge, landscape limitation and ecological conservation. As per the CPCB report 2021, the total wastewater generation in India is 72,368 MLD out of which 72% is discharged untreated into surface water bodies. The sustainable solution to this problem could be innovative water management strategies that integrate technology with landscape design and enhances ecosystem services. Constructed wetlands(CWs) are such treatment systems that…
Read MoreZERO LIQUID DISCHARGE PROJECTS IN CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES
By Ashish Chauhan, Asst. Manager (Process & Project), Lords Chloro Alkali ltd. In recent few years water scarcity is emerging problem in the world. Now days not only in Asian continent but also in European countries like England, Finland faces drought like scenario. Availability of Portable is limited and uneven rainfall made condition more badly. As per Data of water availability around 71% of earth surface is covered with water. In which only 2.5 % is only fresh water out of which only 31% available for us. In recent years…
Read MoreRESPONDING TO EMERGING INFRASTRUCTURE TRENDS IN INDIA WITH BOROUGE’S SUSTAINABLE SOLUTIONS
By Peck Tze Kang, Head of Regional Marketing, Energy & Infrastructure, Asia South, Borouge Projected to become the world’s most populous country in 2023 , India is on the cusp of an energy and infrastructure revolution. The government must ensure its rapidly growing population has access to affordable, reliable, sustainable energy and water. At Borouge, we enable everyday life. As a leading petrochemical company, Borouge provides innovative and differentiated polyolefin solutions for the infrastructure, energy, mobility, advanced packaging, agriculture and healthcare industries. Our solutions also help address several global challenges,…
Read MoreLOW COST OF MLD/ZLD TREATMENT ACHIEVED THROUGH INNOVATIVE BRINE CONCENTRATION MEMBRANES HELPING THE TEXTILE SECTOR
By Tina L. Arrowood, Principal Research Scientist, DuPont Water Solutions, USA and Mahesh Kulkarni, Technical Service and Development Scientist, DuPont Water Solutions, India EXTENDED ABSTRACT For maximizing wastewater reuse and preventing wastewater discharge, zero-liquid discharge (ZLD) is acknowledged for its benefits in protecting fresh surface waters. Unfortunately, it is typically determined to be too expensive to be practical. A more realistic and cost-effective method is a hybrid approach of minimal-liquid discharge (MLD), using reverse osmosis (RO) membranes, to minimize the volume of wastewater prior to thermal ZLD treatment. To comply…
Read MoreMAKES SENSE TO INVEST IN WATER AND SANITATION
By Team EverythingAboutWater Research by Water Aid, an international Ngo focused on water, sanitation and hygiene, states that companies which invest in water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) for their employees, their business thrives. It a well-known fact that water is the essence of life and access to clean drinking water is the ley to a healthy and fruitful life. While we can control, what we consume, when we are at home and that even includes the water that we drink but what does one do when one steps out. Even…
Read MoreWASTE WATER IS A RESOURCE
By Mandar Vaijanapurkar In some cases, energy production has now reached a level where the energy recovered from waste water treatment process not only ensures the plant’s own needs, but also covers the energy needs for drinking, water production and so on. The worldwide consumption of drinking water is doubling every 20 years. At the same time, due to rapid industrialization and exponential growth in population, massive or huge amounts of wastewater is being discharged daily into our environment. However, only close to half of all wastewater is being treated…
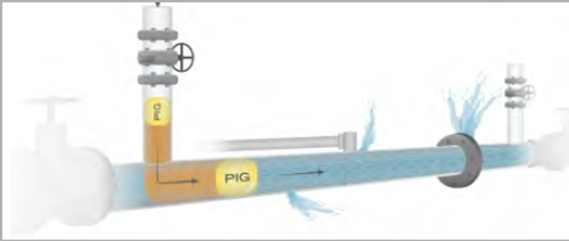
Read MoreTRANSFORMING WATER LOSS INTO A WATER RESOURCE
By Ben Shenkar Presenting a revolutionary new paradigm for repairing distribution Networks with losses, from 25% and above, from within the pipe without the need for leak detection and excavation. Leaks creating water loss in pressurized urban water distribution pipes run rampant both in the developed part of the globe and for India as well, where leakage levels can, in some cases, top even 50% of the water that is distributed. This widespread phenomenon has traditionally been ignored or, at best, token efforts have been made to reduce visual breaks…
Read MoreWATER QUALITY OF GANGA RIVER
By Preeti Shinde, Application Specialist, Hanna Equipments India Pvt. Ltd. The holy river of Ganga is the largest river in India. The Ganges is threatened by severe pollution. This poses a danger not only to humans but also to animals; the Ganges is home to approximately 140 species of fish and 90 species of amphibians. The river also contains reptiles and mammals, including critically endangered species such as the gharial and South Asian river dolphin. The Ganges River Dolphin can only be found in the fresh water rivers of Bangladesh,…
Read More